Every future-oriented company now wants to jump on a bandwagon of blockchain. However, no matter how innovative and game-changing the technology is, it can’t be applied to each business case. Not only can it be inefficient but it can even turn out to be ridiculous and futile, and a mere waste of money. According to our blockchain developers’ advice, before using blockchain technology, you need to understand its underlying functionality and application areas and establish whether they map with your specific business strategies.
There is a discrepancy between what is said about blockchain applications and the practical reality. As a technology, blockchain should be used as the best solution to a certain problem. Instead, we often search for a problem we could solve with blockchain only to join the trend and to be among its first adopters. However, the attempts to apply the technology to a case where it doesn’t make sense will usually cost you a fortune.
Though media says that blockchain offers shiny opportunities, its implementation is rather challenging and risky. Throughout 2016 and 2017 we saw investors growing concerned and dialing back their pace of financing blockchain startups.
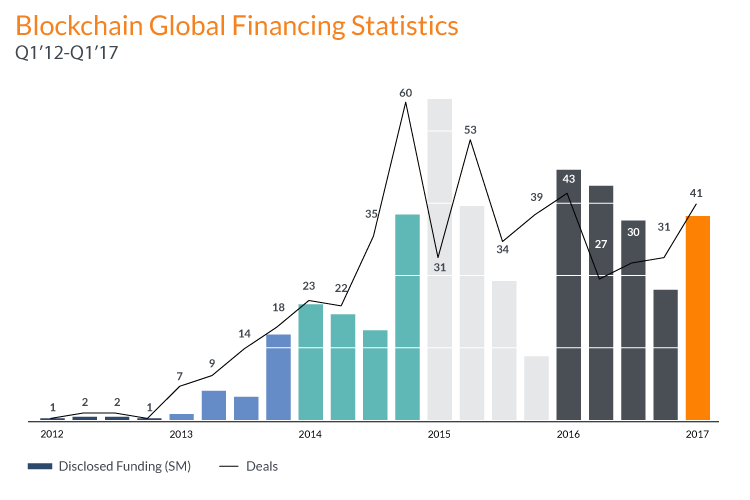
Source: CB Insights
Given the financial risks, it is crucial to weigh up all the pros and cons of applying blockchain technology to a specific business case.
Each time a customer addresses N-iX with a request for a blockchain project, our blockchain developers ask them 3 simple questions:
- What kind of data is to be recorded? Is it permanent or is it subject to changes?
- Do you need each holder of the data to be able to add new records?
- Who are the members of the blockchain and can you trust them?
If the answers are grounded on solid reasons, the decision to use blockchain is valid.
However, to understand those reasons better, you need to have a clear picture of the core characteristics of blockchain, its strategic advantages and disadvantages, and areas of application.
Key characteristics of blockchain :
- Blockchain provides historical data in a chronological sequence and creates a new record of each data input.
- It is a distributed database shared by several or many parties.
- Each member of the blockchain is able to add a new record.
- When a transaction is made, a record of it is written into a “block”. After the block is sealed, it is propagated across the network of computers called ‘’nodes’’.
- Each block contains a hash which links it to the previous block, creating a “chain” of records that is considered impossible to falsify. This helps to validate and sync the data.
- Members of a peer-to-peer network collectively validate new blocks.
- All parties on the blockchain have access to the data, and there is no centralized control over the records.
Blockchain makes sense only if the following conditions are met: you need to record the historical data in a chronological order, you can verify that the sequence of those records is correct, and there are several members to distribute the data among.
Where NOT TO USE blockchain:
- If transaction speed and performance matter to you
Blockchain developers often point out that blockchain-powered solutions typically are not a good fit for instant operations or when performance and speed of transactions are of paramount importance. The issue will be especially acute if there are many members on the blockchain. Since the majority of nodes need to validate a transaction, the more parties there are, the more time-consuming it is. According to blockchain info, the confirmation time may take from about 30 to 1,035 minutes.
- If you are not ready for high costs of development
The price of implementing a blockchain-powered solution is often dozens times higher than developing a standard database because it is a complex technology based on distributed programming.
- If you have privacy and confidentiality concerns
Blockchain may raise potential security issues. Since anyone on the public blockchain has access to the information, it may create risks of corporate espionage. To solve the problem, companies typically build private or consortium blockchains with a limited and predefined number of parties having access to the data.
- If you don’t need a distributed system
Our blockchain developers note that it is reasonable to use this technology only if there are several or many members to distribute the data among.
- If the recorded data is subject to changes
Since the data in the blockchain can’t be changed, each time you input new data or change a slight detail in each transaction, you need to create a new record across the whole network of nodes. That means taking up a lot of expensive storage space for no sound reason.
In many cases, a project can be successfully implemented using a centralized system and traditional databases like Oracle, MySQL, and Postgres or NoSQL databases.
However, blockchain may offer substantial benefits if it is applied sensibly. N-iX blockchain developers have implemented successful projects using this technology, and it has proven to be an effective tool to solve specific tech problems.
Key advantages of blockchain :
- Disintermediation
Blockchain is a good solution when you need several parties to have access to the same data and be in control of it. The code substitutes a central administrator which is needed for managing traditional databases and authenticating transactions. This way blockchains offer a way to replace organizations-intermediaries (governments, universities, banks) with a distributed decentralized system.
- Immutability of records
Blockchain is a distributed ledger of historical data. That means the data recorded into it are not subject to changes. What’s more, the whole network takes part in validating the transactions, and each newly created block contains a timestamp and a hash of the previous block. Thus the records can’t be removed or altered.
- Fault tolerance of the system
The majority of nodes take part in validating every transaction, so no individual node is crucial to the database as a whole. Thus, if an individual node breaks down, that doesn’t do any damage to the overall system.
Where TO USE blockchain:
- Fintech and insurtech transactions are the best fit. The technology is already being actively and successfully used for the development of fintech software solutions. However, in case of public blockchains, it is best applied to lightweight systems where risks for espionage are not high (crowdfunding platforms, gift cards, loyalty programs).
- Shared databases collectively managed by several non-trusting parties (hospital medical records management, notary documents management, state document circulation).
- Decentralized applications for ride-sharing and other Uber-like services. However, if the blockchain comprises many members, transactions may take a lot of time.
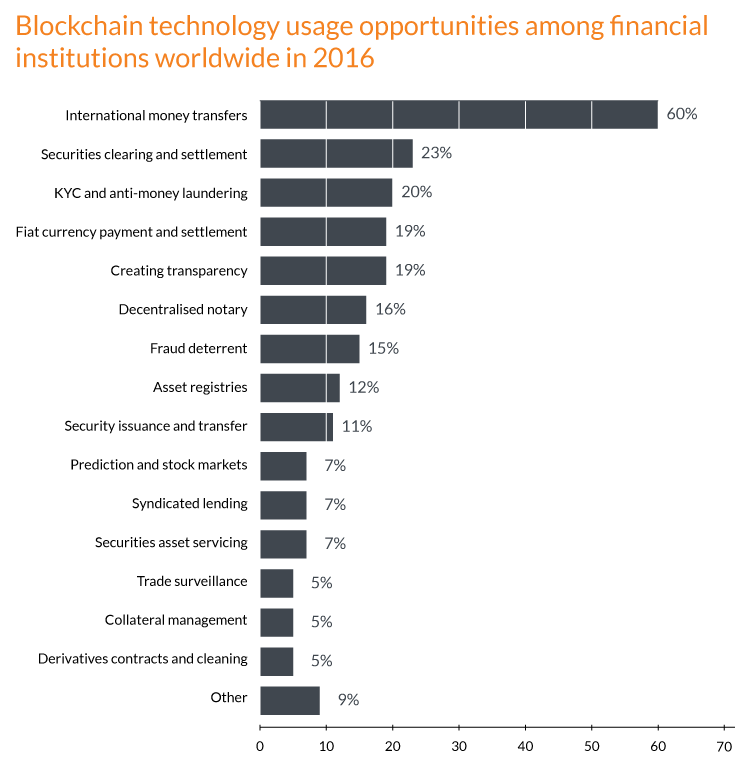
Source: Statista
Read more about the best use cases of blockchain technology in FinTech or explore its implementations in InsurTech.
Wrap-up
We can see a rising trend for blockchain technology, and many market leaders and innovative companies try to leverage its game-changing potential. However, given the expected dimensions of its impact, the technology is still in its nascent stage and suffers from substantial limitations. Its key soft spots are performance problems, confidentiality issues, and high costs of development.
However, blockchain technology offers such tangible benefits as disintermediation, the immutability of records, and fault tolerance, which provide businesses with an unprecedented competitive advantage. N-iX blockchain developers have delivered successful blockchain projects and possess the solid expertise to efficiently apply the technology to each business case.




