As we navigate modern technological solutions, Artificial Intelligence (AI) is a beacon of transformation. It is shaping industries from healthcare and retail to automotive and telecom. One of the examples that has proven to be transformative for enterprises is generative AI. Armed with sophisticated Machine Learning (ML) techniques, this subset of AI can reinvent processes and operations at an enterprise scale. Beyond ChatGPT and Midjourney, what are the primary generative AI use cases? And what benefits and risks do they entail when adopting AI solutions for your company? Let’s figure out the promises, benefits, and limitations of generative AI for business.
What is generative AI?
Generative AI refers to a class of AI systems designed to create new content similar to what humans produce. The examples of content that can be produced include but are not limited to text, visuals, code, audio, and video. Generative AI models are trained on large datasets (billions and even trillions of parameters) by relying upon ML principles.
The result is that generative AI models, either textual or visual, are designed to identify the patterns and data structures and make the most of the pre-trained knowledge to generate new content. The breakthrough of ChatGPT, which reached 100M users in just two months after the launch, has shown an unprecedented interest in generative models. The interest, which, under the right circumstances, can be transformed into business-specific use cases for your organization.
But first, it’s crucial to understand that the rationale behind the generative AI popularity is the ability of these models to leverage various learning approaches. These include unsupervised, semi-supervised, and reinforcement learning with human feedback (RLHF). For instance, here is how the RLHF method was used to train the ChatGPT model.

One crucial moment to remember is that the interest in generative AI use cases goes beyond individual users and curious tech-savvies. Tech giants like OpenAI (GPT-4, DALLE-2, Whisper), Google (PaLM 2), Microsoft (Bing with GPT-4 integration), Meta (LLaMA), GitHub (Copilot), Anthropic (Claude), Stability (Stable Diffusion), and Amazon (CodeWhisperer) are only a few examples of companies of implementing their custom generative AI solutions. These enterprises, alongside individual large language model (LLM) researchers, have significantly contributed to advancing AI and ML technologies to the general public.
Why should you care about generative AI?
While the subject matter is at its height in terms of popularity, businesses often find it hard to gain the most value from it. Let’s review the enterprise insights that vividly showcase how generative AI use cases already revolutionize the industry. A recent report by Salesforce indicates that 57% of IT leaders believe that AI is a game-changer. Moreover, Gartner showcases revenue growth (26%) and cost optimization (17%) as the primary purpose of generative AI investments among business executives.
On the scale of employee productivity and broader economic forecast, a study by McKinsey expects 75% of all the value that generative AI use cases could deliver falls into customer operations, marketing and sales, software engineering, and R&D. Generative AI could enable an annual labor productivity growth of 0.1% to 0.6% by 2040. These insights, combined with the renewed interest in adopting the enterprise scale, encourage businesses to find ways to make the most of this technology. So, what can generative AI bring to the table for your business? Let’s find out.
Benefits of generative AI
AI significantly impacts various facets of business operations, from customer service to data operations. Through practical examples, this section will highlight the capacity of generative AI to enhance operational efficiency, boost innovation, and reduce workload.
Reinventing customer service
Generative AI models such as chatbots and virtual assistants revolutionize customer service, providing prompt and practical support. A prime example is the AWS Contact Centre, which utilizes AI to automate responses to common inquiries. This system ensures increased customer satisfaction by reducing wait times and decreasing the time to solution. On the business side, you’ll reduce operational costs and speed up customer sentiment identification. More specifically, AWS Contact Centre solutions cover three crucial use cases:

Streamlining software engineering
For software engineers, tools like GitHub Copilot can be utilized to automate repetitive tasks. Some possible applications include getting natural language prompts and performing code reviews. All of this, in turn, can result in development time optimization and an increase in the productivity of engineering teams. Software developers using generative AI tools can also automatically generate or auto-complete data tables and synthetic data.
Automating marketing content creation
Text-based models can be used to create a wide variety of content, such as blog posts, social media posts, articles, and more, thereby saving companies considerable time and resources. Fine-tuned models trained on proprietary data can be trained to mimic a company's style and tone, allowing for a consistent brand voice across all forms of communication. Designers and brand managers also use state-of-the-art visual systems like Stable Diffusion and Midjourney for visual content generation.
Using data for your competitive advantage
In the age of Big Data solutions, businesses generate enormous amounts of information daily. However, you can get its potential value if you use the tools to analyze and interpret it. Generative AI, thanks to its ability to understand and recognize patterns, can turn raw information into actionable insights. It can predict consumer behavior, identify market trends, and provide strategic recommendations, enabling businesses to make more informed, data-driven decisions.
Reducing employee workload
Generative AI can significantly reduce employee workload by taking over routine tasks. This increases productivity as employees can focus on more complex and impactful tasks. Additionally, by reducing the burden of monotonous tasks, AI can prevent employee burnout. Simply put, generative AI can boost worker productivity while reducing employee turnover and increasing customer satisfaction.

Generative AI: Key use cases
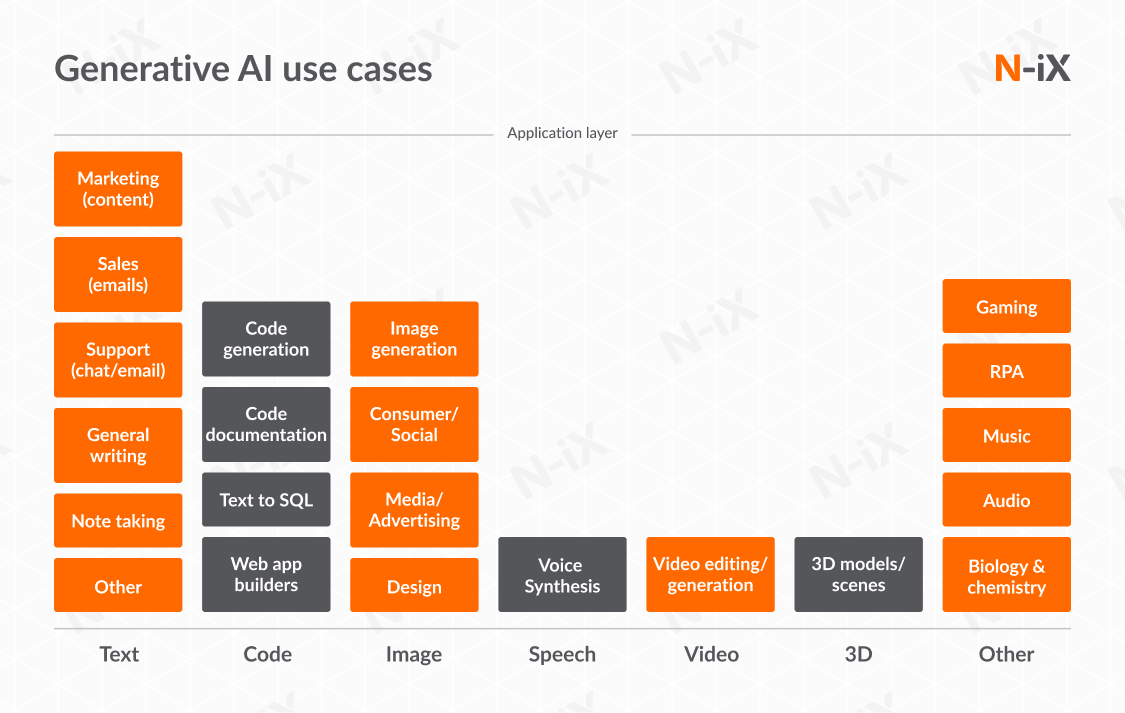
Organizations need to be familiar with the current application landscape to move forward with generative AI in business. In other words, what are the specific use cases based on what you’re working with? Encompassing a range of applications, from text and code to image and speech, here are the most popular generative AI use cases based on the types of inputs:
1. Text
Generative AI models like GPT-4 have demonstrated an impressive ability to generate human-like text. The text outputs are used in creating responsive chatbots, automated email replies, content generation for blogs and websites, personalized marketing campaigns, and drafting reports. For enterprises, language-based generative models can assist in writing marketing and sales copies, creating product user guides, improving sales through chatbots, and optimizing content strategies.
2. Code
Automating code and documentation writing, converting text to SQL, and using web app builders have an untapped potential for boosting engineering productivity. One such instance is using GitHub’s Copilot, which suggests lines of code or entire functions, effectively serving as an AI pair programmer. On top of that, a recent release of Code Interpreter within GPT-4, which serves as a built-in Python compiler, has shown that the model can visualize data and perform an array of data engineering workloads.
3. Image
Through techniques like Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs), AI generative models can create unique images or alter existing ones. The range of applications is limitless, helping creative specialists to create new designs, concepts, or full-fledged graphics. This can help in brainstorming, prototyping, and even producing final products. Companies like Stability and Midjourney continually update their products, making imagery generation even more advanced. Overall, the use cases in the image inputs include but are not limited to social media, advertising, and design.
4. Speech
One of the most impressive breakthroughs in generative AI is the introduction of speech-to-text models, like Whisper by OpenAI. These applications can synthesize human-like speech or create personalized customer experiences using voice cloning. On top of that, transcription services can convert spoken content into text, which helps generate written records of meetings, conferences, or customer service calls. These applications significantly affect customer service, potentially increasing the productivity of customer service operations by 30% to 50% if implemented on scale.
5. Video
AI can also generate video content, which can be used for virtual reality experiences, movie special effects, and more. Media and advertising enterprises can use AI to generate new video content or edit existing footage, speeding up production and allowing for more creativity.
6. 3D
Manufacturing and design firms can use AI to generate 3D models from sketches or existing designs, streamlining the prototyping process. AI can also test and refine these designs, simulating their functionality under different conditions. This can be especially useful in fields like architecture, product design, and manufacturing, where 3D models play a crucial role in design and prototyping.
7. Other
Generative AI has even more diverse applications, including the RPA systems that automate repetitive tasks, generate sound effects or entire audio landscapes, make gaming NPCs more conversational and intelligent, and generate molecular structures for drug discovery. With generative AI and its rapid growth and scalability potential, we will see even more breakthroughs in enterprise use cases.
Generative AI use cases across industries
The applications of generative AI are not confined to a specific industry but span numerous sectors. Here are some of the many ways different industries can leverage generative AI.
Retail & e-commerce
Personalization is vital in this sector. It can be achieved through AI algorithms generating unique product recommendations tailored to each customer's purchasing history and preferences. This enhances the shopping experience and boosts conversion rates and customer loyalty.
Furthermore, AI can generate creative, engaging product descriptions, reducing the burden on copywriters and ensuring a consistent brand voice across thousands of product lines. Additionally, generative AI can create lifelike product images or even 3D models from simple sketches or descriptions, allowing potential customers to visualize items before purchase, thus enhancing the overall user experience and driving sales.
Automotive
AI in the automotive industry can generate diverse design options based on initial specifications, facilitating a more efficient, creative process for new vehicle models. AI can simulate these designs' performance under different conditions, helping engineers refine them before physical prototyping, saving time and costs. Generative AI can also assist in creating virtual environments for testing autonomous driving systems, producing realistic traffic scenarios, weather conditions, or unexpected obstacles, thus improving the safety and reliability of self-driving technology.
Read more: AI in the automotive industry: Fueling a smarter, safer driving experience
Healthcare
Generative AI holds transformative potential for healthcare. It can accelerate the drug discovery process by generating potential molecular structures for new medications, vastly reducing the time and resources needed compared to traditional research methods.
AI can also create 3D models from medical imaging data, helping physicians visualize health issues more accurately and plan treatments more effectively. These models can be used in teaching, allowing students to explore the human anatomy interactively. AI-generated virtual scenarios can also be used for surgical training, allowing clinicians to practice procedures in a risk-free environment.
Finance
Modern AI models can estimate different economic scenarios, aiding analysts in predicting market trends and making informed investment decisions. AI can automate financial advice, generating personalized investment strategies for clients based on their financial goals and risk tolerance. For instance, the release of BloombergGPT, which can be used for data search and analysis, creating custom reports, and generating market insights, has proven that the financial industry's interest in LLMs has grown exponentially.
Generative AI can simulate many risk scenarios in risk management, helping firms better prepare for potential market downturns. Insurance companies can also significantly benefit from the application of generative AI solutions. Some possible applications include generating personalized insurance plans based on individual clients' data and risk profiles.
Read more: How AI in fintech takes the industry forward
Communications & media
Some possible use cases include generating content for news articles, press releases, or social media posts, allowing companies to maintain an active online presence and engage their audiences more effectively. For broadcasters and video production companies, AI can assist in creating realistic CGI or special effects, speeding up the post-production process and enabling more creativity.
AI can also generate radio, TV shows, or movie scripts, assisting writers with plot development, dialogue creation, and character progression. Businesses can create personalized advertising content, targeting individual viewers' preferences and viewing history, enhancing viewer engagement and ad effectiveness.
Telecommunications
Generative AI can revolutionize several facets of the telecom sector. Network optimization, a significant challenge in this industry, can be streamlined using AI to simulate different network configurations and their performance under varied traffic loads. This helps in achieving optimal network design and improved quality of service.
Furthermore, AI can assist in network maintenance, identifying potential failures before they occur and suggesting corrective measures. This proactive approach reduces downtime, thereby improving customer satisfaction.
These are just a few examples of how generative AI can be applied across industries. As the technology continues to evolve, its applications are expected to expand further, potentially transforming how businesses operate in every sector.
Read more: AI in telecommunications: uses, challenges, best practices
Generative AI risks and how to address them
Accuracy and unintended biases
AI models are trained using existing data, and if this data contains biases, the AI can also exhibit these biases in its outputs. AI models can sometimes produce inaccurate results or "hallucinations"– when AI generates content unrelated to the input or misrepresents the data. This can lead to confusion or misinterpretation, particularly when AI is used in critical areas like decision-making or customer communication.
Solution: Businesses must employ rigorous validation methods to use the output data properly. If you plan to use a foundation model trained on proprietary data, employing model validation methods using diverse datasets is necessary.
Data privacy and security
AI systems are typically trained on vast amounts of data, sometimes including sensitive or personal information. There's a risk that these models could inadvertently reveal this information in their outputs, breaching privacy regulations and damaging trust.
Solution: Addressing this risk requires robust data-handling practices. Enforcing the generative AI usage policy on the enterprise scale is crucial to ensure sensitive data compliance.
Intellectual property
As AI begins to generate content, from writing to music to artwork, it brings into question the matter of intellectual property. Who owns AI-generated content? What happens when AI creates something that closely resembles a human-created piece? These are complex questions that challenge our current understanding of copyright laws.
Solution: Clear guidelines and regulations around the ownership of AI-generated content are needed to address this. Businesses should also have transparent conversations with stakeholders about using AI and its implications for intellectual property.
Over-reliance on foundation models
For companies to gain a real competitive advantage in the era of AI, it's essential to move beyond using pre-trained models of other companies. Investing in creating proprietary large language models with RLHF methods could provide unique insights and capabilities tailored to the business's needs.
Solution: Creating the foundation model requires a significant investment in data collection, model training, and ongoing updates. It also requires strong data governance practices to protect the value of proprietary data.
Lack of qualified ML engineers
As the demand for AI capabilities grows, there's a widening gap in the availability of skilled ML engineers and solutions architects who can design, deploy, and maintain these complex systems.
Solution: Businesses can invest in training and upskilling their current workforce. Additionally, partnerships with technology leaders with sufficient expertise in the field can facilitate access to emerging talent and cutting-edge research. For instance, by partnering with N-iX, a global software solutions and engineering services company, you can partner on conducting a Discovery Phase to kick off the work on your generative AI solution.
While generative AI use cases are vast, these tools also carry certain risks. Yet, these can be effectively mitigated with careful management and proactive strategies. The key lies in balancing the potential with responsible practices that ensure accuracy, privacy, and respect for intellectual property.

Bottom line
Generative AI is a thriving field with the potential to disrupt industries and redefine our operations. Despite the risks and challenges, generative AI could unlock new paradigms in efficiency, creativity, and operational effectiveness with the proper measures and regulations in place. Continued research, development, and open discussion about the ethical use of these technologies will be crucial to maximize their potential while minimizing potential risks. As we at N-iX venture further into the era of generative AI consulting, it is clear that generative models will play a pivotal role in shaping the digital future for our clients.
Have a question?
Speak to an expert




