The rapid adoption of cloud solutions is reflected in the anticipated 20.4% surge in global cloud market growth, reaching $2.39T by 2030[1]. However, this accelerated move toward cloud-first approaches introduces a new set of complex security challenges. Experts predict a rise in sophisticated cyberattacks targeting cloud architecture and infrastructure vulnerabilities in 2026. Cloud security trends like AI-powered threat detection, Zero Trust principles for access control, robust encryption, and others can help you optimize your cloud security.
8 cloud security trends in 2026
Security professionals reported a 54% increase in direct attacks on cloud infrastructure in the latest Thales cloud security study [2]. At the same time, 55% of respondents in the report said protecting cloud environments presents greater challenges than securing on-premises infrastructure. To help you manage vulnerabilities and threats, our experts share the key technologies to help you protect your cloud in 2026.

1. AI's increasing role in securing cloud environments
AI and ML are emerging trends in cloud security, enabling teams to address sophisticated cloud computing challenges. This is why many experts see cloud security as the area where defensive AI will have the biggest impact. It is reported by 66,4% security specialists in the latest State of AI Cybersecurity Report by Darktrace [3].
Security engineers use AI for its ability to analyze vast datasets at high speeds and for significant advantages in detecting and mitigating threats. The main use cases of AI cloud security are:
- Enhanced threat detection and prevention: Real-time analysis of massive datasets allows AI and ML to identify abnormal behavior indicative of cyber threats. By recognizing attack patterns more quickly, these systems can prevent breaches before they occur.
- Proactive behavioral analysis: ML algorithms establish baselines of normal user behavior, enabling them to detect deviations that might signify unauthorized access or insider threats. This proactive approach offers increased vigilance against internal risks.
- Automated response: Upon threat detection, AI-powered systems can take immediate action. This might involve isolating compromised systems, blocking suspicious IP addresses, or quarantining malware, offering rapid response capabilities.
- Predictive security measures: Machine Learning models leverage historical data to predict future attack trends. This predictive analysis empowers organizations to implement security measures before potential threats emerge.
Although AI is becoming more widespread and accessible, it also exposes cloud computing to a broader range of security risks. Google's Secure AI Framework (SAIF) and NIST's AI risk management framework offer valuable principles for safeguarding cloud-based AI. Implementing these principles ensures trustworthiness and minimizes common vulnerabilities.

Secure your cloud with 10 best practices—get the guide now!


Success!

2. Implementing the Zero Trust model
Zero Trust is one of the networking cloud security services trends that minimizes risk and enhances protection. This approach breaks away from the traditional "perimeter defense." Instead, it continuously verifies users, devices, and applications before granting network access, no matter their location or perceived trustworthiness. While Zero Trust has been promoted by the US government and others since 2010, its widespread implementation has yet to be fully realized.
Notably, adopting Zero Trust principles has been more successful in cloud architecture, primarily among cloud service providers (CSPs). The reasons why CSPs have a significant advantage over traditional hardware and software vendors in implementing Zero Trust are:
- Control over software stack: CSPs have complete control over their software stack, eliminating the need for separate network monitoring, multi-factor authentication, and OS monitoring. They integrate, coordinate, and correlate everything within their stack.
- Control over the hardware stack: CSPs often build their own hardware, including CPUs and network devices, to control the entire stack. This integration streamlines security measures.
- Close monitoring of entry points: All activities are closely monitored when users connect to a CSP. This vigilant monitoring enables CSPs to detect anomalous behavior promptly, potentially identifying breaches before they affect their clients.
The latest Zero Trust report by StrongDM reveals that 84% of cybersecurity engineers are actively implementing Zero Trust principles for cloud infrastructure security. Among them, 64% also prioritize identity and access management (IAM) and data encryption to strengthen this approach [4]. Zero Trust is also driving advancements in biometrics, multi-factor authentication (MFA), and IAM 2.0. The last complements traditional IAM controls with AI and ML capabilities for smarter and adaptive cloud security.
3. Cybersecurity mesh architecture (CSMA)
Cybersecurity mesh is a strategy that protects each device independently, leveraging its perimeter defenses, such as firewalls and network protection tools. Unlike traditional security practices that rely on a single perimeter for the entire IT environment, security mesh employs a holistic approach. Coined by Gartner as "cybersecurity mesh architecture" (CSMA), this concept is becoming increasingly important within cloud security future trends, especially as more assets move into multi-cloud environments. It emphasizes viewing security as a platform where all components work together seamlessly.
CSMA enables organizations to reduce vendor footprint while deploying best-in-class solutions through integration. It represents a significant shift from traditional perimeter-based security models toward a decentralized, device-centric approach to network security.

4. Secure access server edge
One of the new trends in cloud security, secure access server edge (SASE), consolidates network and security functions into a single, cloud-delivered service. This helps reduce costs, streamline management, and improve performance by replacing traditional "hub and spoke" architectures with secure access regardless of user location. By combining Secure Web Gateway, Firewall as a Service, and Zero Trust Network Access, SASE delivers lower costs, enhanced security, and optimized staff workloads.
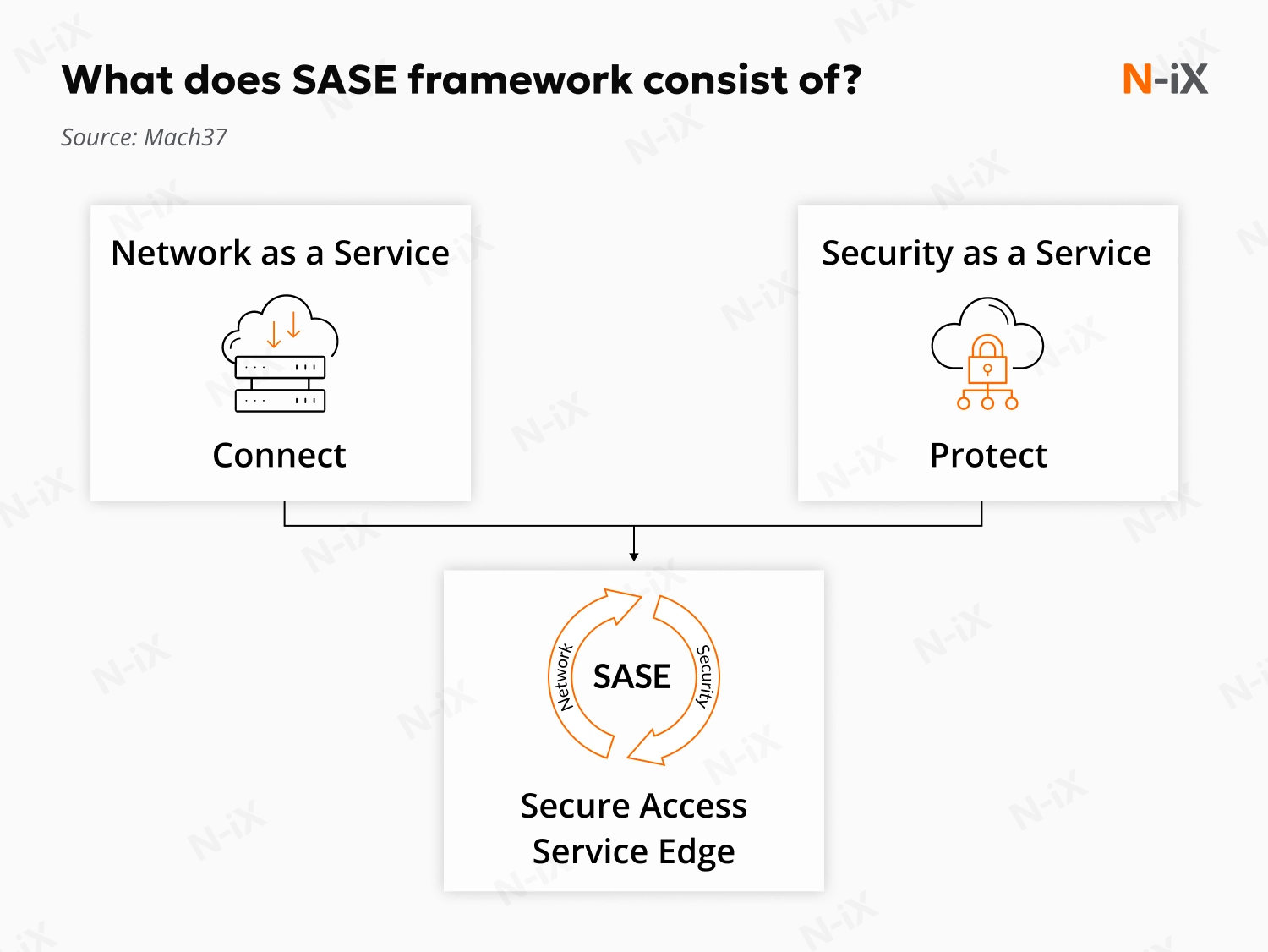
By 2028, Gartner predicts that 70% of software-defined wide-area network (SD-WAN) purchases will be bundled with a single-vendor SASE platform, up from 25% in 2025. Additionally, half of all new SASE implementations are expected to rely on single-vendor solutions, up from 30% in 2025 [5]. This reflects a clear movement in cloud security trends toward consolidating and streamlining IT infrastructure.
5. Automation of DevSecOps
DevSecOps emphasizes making security a shared responsibility among developers, operations teams, and security experts. DevSecOps automation takes this a step further by providing the right tools to ensure secure code and configurations without requiring everyone to be a security specialist. This approach automates security integration into DevOps, continuous integration, and continuous deployment (CI/CD) pipelines. As a result, it significantly reduces the errors that can occur during manual security analysis.
This trend aligns perfectly with the broader shift towards proactive security, enabling teams to embed security into the software development lifecycle from the beginning.
6. Cloud-native protection platforms (CNAPPs) and tools
One of the major cloud security trends is the growing use of cloud-native application protection platforms (CNAPPs) and tools. These technologies are built to defend cloud containers, APIs, and microservices at every stage.
This shift is gaining speed because today's cloud environments demand more connected security tools. According to Gartner's forecast, by 2029, 40% of organizations that successfully adopt Zero Trust in the cloud will rely on the powerful visibility and control that CNAPPs provide [6]. This means CNAPPs will be among the cloud-native security trends in the future, helping companies build safer cloud systems that meet modern security standards.
CNAPPs are still relatively new, but they are gaining traction as companies embrace cloud-native development and seek better ways to secure their applications. Traditionally, companies used isolated tools for security tasks, such as code scanning or cloud posture management. CNAPPs combine these functions into one platform, making it easier to manage application security holistically.
Read more: 12 cloud computing trends reshaping the industry in 2026
7. Enhanced data encryption
As cloud adoption grows, protecting sensitive data has never been more critical. In 2025, an estimated 54% of cloud-stored data is classified as sensitive [2], underscoring the need for stronger encryption methods. One of the most promising innovations is confidential computing, which uses trusted execution environments (TEEs) to protect data while it's being processed, rather than only when it's stored or transmitted. This approach minimizes exposure during computation, reducing the risk of data leaks or unauthorized access.
Another crucial development is quantum-safe cryptography. As quantum computing advances, it poses a future threat to traditional encryption methods, potentially rendering them obsolete. In response, quantum-safe algorithms are being designed to withstand the power of quantum attacks, ensuring long-term data security.
One of the most recent trends in cloud security is homomorphic encryption. It is an approach that allows computations to be performed on encrypted data without first decrypting it. This is a game-changer for industries that require secure data analysis, such as healthcare and finance, as it enables sensitive data to be used for analytics without compromising its privacy.
8. Focus on regulatory compliance
Regulatory compliance remains one of the key cloud computing security trends as organizations worldwide face increasingly stringent data protection requirements. Ensuring that cloud environments meet evolving laws is essential not only to avoid penalties but also to maintain customer trust and safeguard sensitive information.
In this context, sovereign cloud and data governance play a central role. Sovereign cloud solutions give organizations complete control over where their data is stored and processed, ensuring it remains within specific national or regional boundaries. This helps organizations comply with local regulations and maintain transparency over cloud operations. Meanwhile, strong data governance ensures that cloud data is properly classified, monitored, and managed throughout its lifecycle. Together, these practices enable organizations to build secure, compliant cloud architectures that meet regulatory requirements.
Why choose N-iX as your cloud security partner?
Embracing the latest market trends in cloud security can be complex without expert guidance. Partnering with an experienced consultant can streamline the implementation of effective security practices and help avoid common pitfalls.
N-iX is a trusted partner in cloud security with over 23 years of industry experience. Our team of 400+ cloud engineers has delivered over 150 successful cloud projects within the past five years. As an AWS Premier Tier Services Partner, Microsoft Solutions Partner, and Google Cloud Platform Partner, N-iX brings deep platform-specific expertise to secure cloud environments across providers.
N-iX adheres to leading security standards, including PCI DSS, ISO 9001, ISO 27001, and GDPR, to protect your data at every stage. Our teams apply strong security practices and help organizations build compliant cloud solutions that strengthen customer trust and reduce reputational risks.
Adopt cloud security trends with N-iX now to defend your future cloud solutions with confidence.
References
- Grand View Research - Global Cloud Computing Market Size & Outlook, 2025-2030
- Thales - 2025 Thales Cloud Security Study
- Darktrace - The State of AI Cybersecurity 2025 report
- StrongDM - The State of Zero Trust Security in the Cloud 2025 Survey
- Gartner Research - Gartner Magic Quadrant for SASE Platforms 2025
- Gartner - 2025 Market Guide for CNAPPs
Have a question?
Speak to an expert